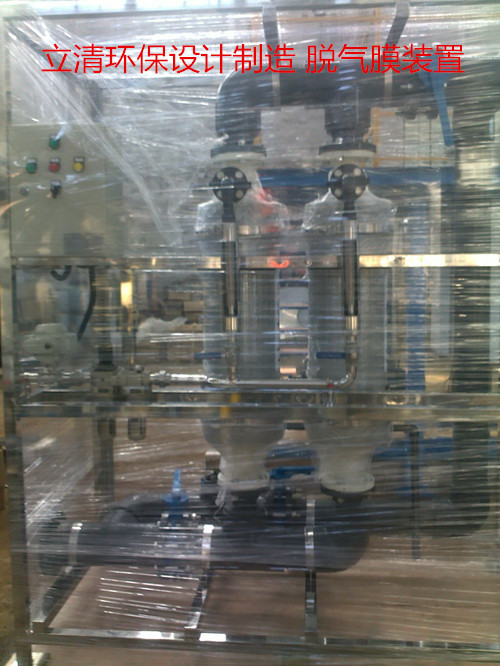
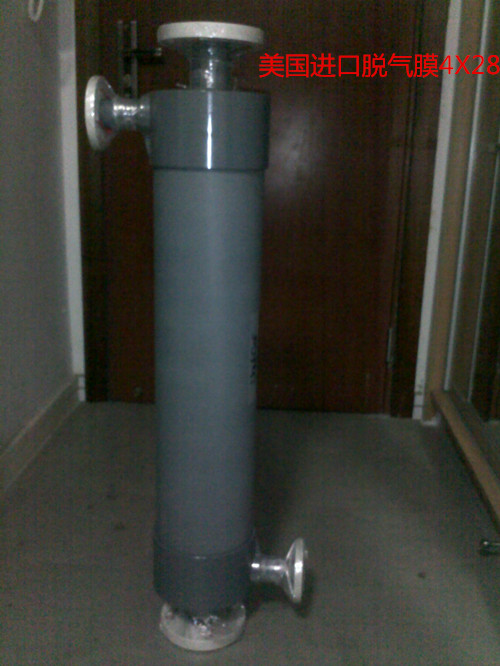
制药工业需要连续不断的纯水源,其导电率小于1.3 µS/cm。 控制和去除水中溶解的CO2将可使水达到这一导电率水平。 历史上,带有NaOH化学药品被用来控制CO2 现在,人们不再使用化学药品,因为它们对环境有负面影响,而且对处理这些化学药品的人存在安全隐患。 此外,EDI 和 CDI 已成为制药工业中离子交换的普遍技术。 如果提前将溶解的CO2从水中去除,这些技术能够更加有效地实施。 水中过多的 CO2 将加重 EDI 的负担,而且与必需的EDI膜堆相比,需要更多。 制药工业同样也需要没有 污染物的高水质。 Liqui-Cel膜组件为制药工业中的气体控制提供了一个理想的解决方案。 Liqui-Cel系统是封闭系统,不在水中引入环境污染物,就像早先的强制通风脱气器所作的一样。 它们也可以替代使用化学溶液的压注。 膜组件也可同时去除O2 和 CO2 ,这对于任何氧气对最终产品有负面影响的过程都有好处。 有时候,氧气会影响保存期限和产品稳定性。 接触器提供了一个简便的气体去除系统,可以每天无故障地运行24小时,一周运行7天。
Membrane contactors
reduce chemical use and blowdowns
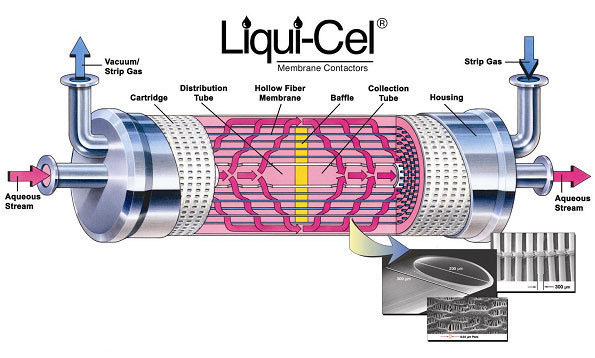
Schematic of the
Liqui-Cel Membrane
Contactor
Provided by Membrana
Proper treatment of boiler
feedwater is an important
part of operating and main-
taining a boiler system. As steam is
produced, dissolved solids become
concentrated and form deposits
inside the boiler, leading to
poor heat transfer and
reduction of boiler efficiency.
Dissolved gasses, such as
oxygen and carbon dioxide,
react with metals in the boiler
system, resulting in boiler corrosion.
These gasses should be controlled or
removed to protect the boiler.
Several different technologies are
widely used in the industry to remove
these contaminants. Reverse osmosis
membrane and ion exchange systems
can remove dissolved solids. Forced
draft degasifiers, chemical agents and
steam de-aerators have historically
been used to remove dissolved gasses.
Membrane contactors are increas-
ingly being used to remove dissolved
gasses in boiler feedwater. Widely
used in the semiconductor, power,
pharmaceutical and other industries to
control dissolved gasses in water
systems, their use in boiler feedwater
degasification systems has grown
steadily since the development of new
industrial grade devices.
Membrane contactors contain micro-
porous hydrophobic membranes,
which are used to bring gas and
liquids in direct contact without
mixing. Contactors operate by
lowering the pressure of gas in contact
with the liquid to create a driving force
to remove the dissolved gasses from
the water. They are highly efficient and
compact, and can be used inline under
pressure.
Chemical treatment
Chemical treatment is widely used to
control dissolved oxygen in a boiler.
The cost of operating a chemical
treatment program consists of chemical
costs and blow down costs. As the
water is converted to steam, non-
volatile compounds in the boiler feed
water are concentrated inside the
boiler. Periodically the water in the
boiler must be flushed out to remove
these compounds by a process called
blow down. Any chemical that is
added to the water can increase the
frequency of blow down, which affects
operating costs of the boiler.
The cost of blow down can be broken
down into two costs – water and
heat/energy. First, water and steam
that is purged from the boiler during
blow down is drained, so this water
must be replenished by fresh makeup
water. Second, the water blow down
from the boiler is hot and is replaced
with cold water that must be reheated
to produce steam. Energy costs can be
calculated by looking at the energy
needed to heat the water back to the
temperature of the steam produced by
the boiler.
In smaller low-pressure boilers
(<10,000 lbs/hr and < 50 psig),
chemical treatment alone may be used;
a combination of steam deareation and
chemicals is most often used
for larger high-
pressure boilers. For ease of calculation,
a small low-pressure boiler using a
chemical program only will be eval-
uated in this paper. These same calcula-
tions can be used to evaluate boilers
that use steam deareation. When evalu-
ating a deareator, the cost of operation
should also be included. The operating
cost of the steam deareator can be esti-
mated by calculating the extra feed
water required to operate the deareator
and the energy loss associated with
venting the steam deareator.
In practice, 10 ppm of pure sodium
sulfite is needed to remove one ppm of
oxygen from water. One ppm of
sodium sulfite equates to 8.3 lbs per
million gallons of water. The amount
of dissolved oxygen in the water varies
with the water temperature. If 10 ppm
of oxygen is dissolved in the water,
83.0 lbs of sodium sulfite will be
Any chemical that is added
to the water can increase the frequency of
blow down, which affects operating costs of
the boiler. Fred Wiesler, Membrana
Liqui-Cel
® Membrane
Contactors degasify boiler feed
water, reduce chemical use and
blowdown frequency, resulting
in lower operating costs.
Table 1
Boiler Operating Details
Chemically Treated Feed Water Degassed Feed Water
Boiler capacity 10,000 lb/hr 10,000 lb/hr
Pressure 50 psig 50 psig
Efficiency 80% 80%
Fuel Natural Gas Natural Gas
Fuel cost 4.5 USD/ 1000 ft
3
4.5 USD/ 1000 ft
3
Fuel efficiency 1000 BTU/ft
3
1000 BTU/ft
3
Condensate return 30% 30%
Boiler blow down rate 10% 5%
Hours of operation 6600 hrs/yr (275 days/yr) 6600 hrs/yr (275 days/yr)
Feed water costs 1.2 USD/1000 gallons 1.2 USD/1000 gallons
Sodium Sulfite cost 0.5 USD/lb 0.5 USD/lb
Feed water temperature 60º F 60º F
Inlet Dissolved 9.0 ppm 0.5 ppm
Copyright 2004 by PennWell